What Is Ecological Restoration?
Our natural areas are in urgent need of support. Learn how we can make an impact through ecological restoration in our communities.
What Is Coastal Erosion?
Coastal erosion is a natural, ongoing process that has been happening for thousands of years. This video explains how it happens and the factors that affect the rate of erosion.
What Is A Wetland?
Wetlands are areas where water covers the soil, or is present either at or near the surface of the soil all year or for varying periods of time during the year, including during the growing season. Water saturation (hydrology) largely determines how the soil develops and the types of plant and animal communities living in and on the soil. Wetlands may support both aquatic and terrestrial species. The prolonged presence of water creates conditions that favor the growth of specially adapted plants (hydrophytes) and promote the development of characteristic wetland (hydric) soils.
What Is A Watershed?
This animated video explains "how watersheds work in the United States and how they impact us on many levels."
What Is A Watershed
Watershed concepts are vital to include in any conversation about water pollution. This animated video explains "how watersheds work in the United States and how they impact us on many levels."
Wetland Restoration Techniques
In this webinar hosted by Thomas R. Biebighauser, you will learn about the techniques used in wetland restoration, as well as some examples of their application. This webinar was produced as part of the Wetlands Institute Speaker Series.
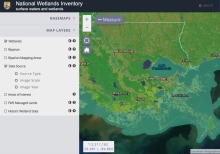
Wetlands Mapper
The Wetlands mapper is designed to deliver easy-to-use, map like views of America's Wetland resources. It integrates digital map data along with other resource information to produce current information on the status, extent, characteristics and functions of wetlands, riparian, and deepwater habitats. The Wetland Mapper fulfills the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service's strategic plan for the development, revision and dissemination of wetlands data and information to resource managers and the public.
Wetlands Mitigation Rules Get Tougher, And St. Tammany Officials Get Worried
Land was chosen and a road was developed, but the grocery store was never built after the Army Corps of Engineers changed the wetlands mitigation rules. The deal fell victim to stringent new requirements by the Army Corps of Engineers that forces developers to pay more to offset the loss of wetlands in new construction projects. And with much of St. Tammany Parish -- even the acres of pine forest that appear high and dry to the naked eye -- classified as wetlands by the corps, local leaders fear the tough new restrictions will stifle growth for years to come.
What Are Microplastics?
Microplastics come from a variety of sources, including from larger plastic debris that degrades into smaller and smaller pieces. In addition, microbeads, a type of microplastic, are very tiny pieces of manufactured polyethylene plastic that are added as exfoliants to health and beauty products, such as some cleansers and toothpastes. These tiny particles easily pass through water filtration systems and end up in the ocean and Great Lakes, posing a potential threat to aquatic life.
Pagination
- Previous page
- Page 15
- Next page