Using Sediment Enhancing To Build Tidal Marsh Resiliency On Blackwater National Wildlife Refuge
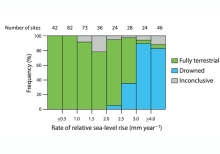
"Located in Maryland, USA, Blackwater National Wildlife Refuge is part of the largest area of tidal marsh within the Chesapeake Bay watershed, and is of regional ecological significance for its wetlands and for the wildlife populations it supports. However, over 5,000 acres of tidal marsh have converted to open water on the refuge since 1938... In December 2016, 26,000 cubic yards of sediment was pumped in a thin-layer application over approximately 40 acres of tidal marsh on the refuge. The purpose of this project is to raise the elevation of the existing marsh platform."