Resource Category
Resource Subject
Resource Content Type
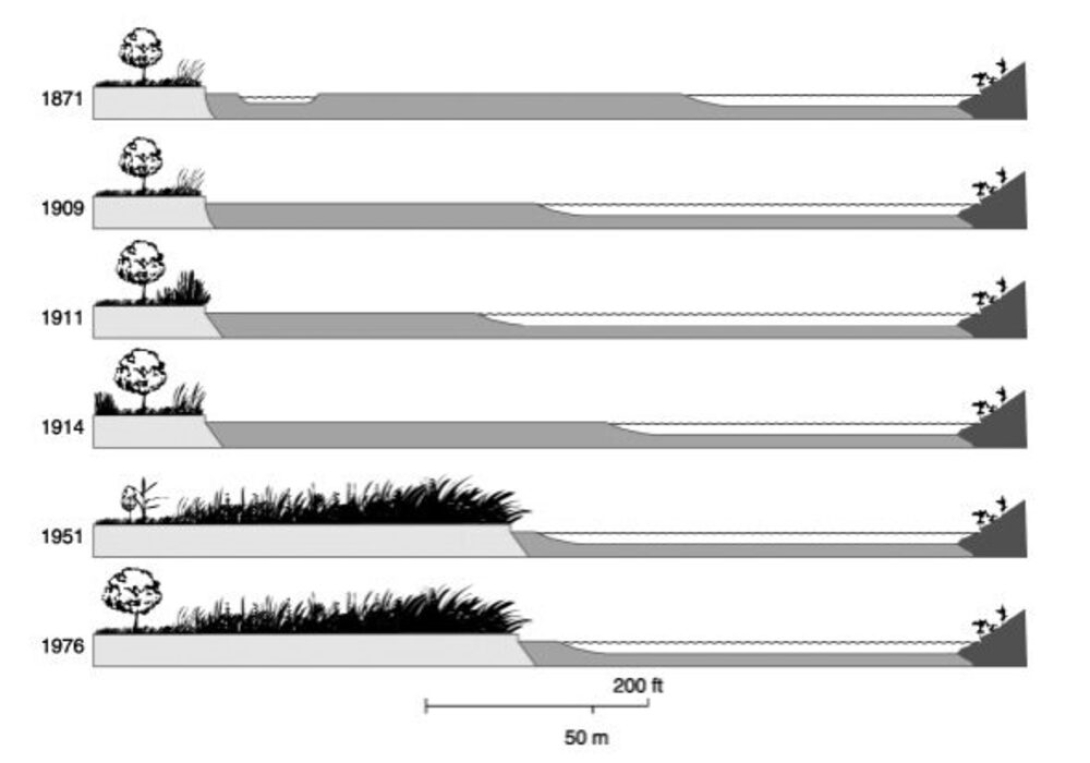
Wetlands seem to be especially vulnerable to invasions. Even though ?6% of the earth's land mass is wetland, 24% (8 of 33) of the world's most invasive plants are wetland species. Furthermore, many wetland invaders form monotypes, which alter habitat structure, lower biodiversity (both number and "quality" of species), change nutrient cycling and productivity (often increasing it), and modify food webs. Wetlands are landscape sinks, which accumulate debris, sediments, water, and nutrients, all of which facilitate invasions by creating canopy gaps or accelerating the growth of opportunistic plant species.