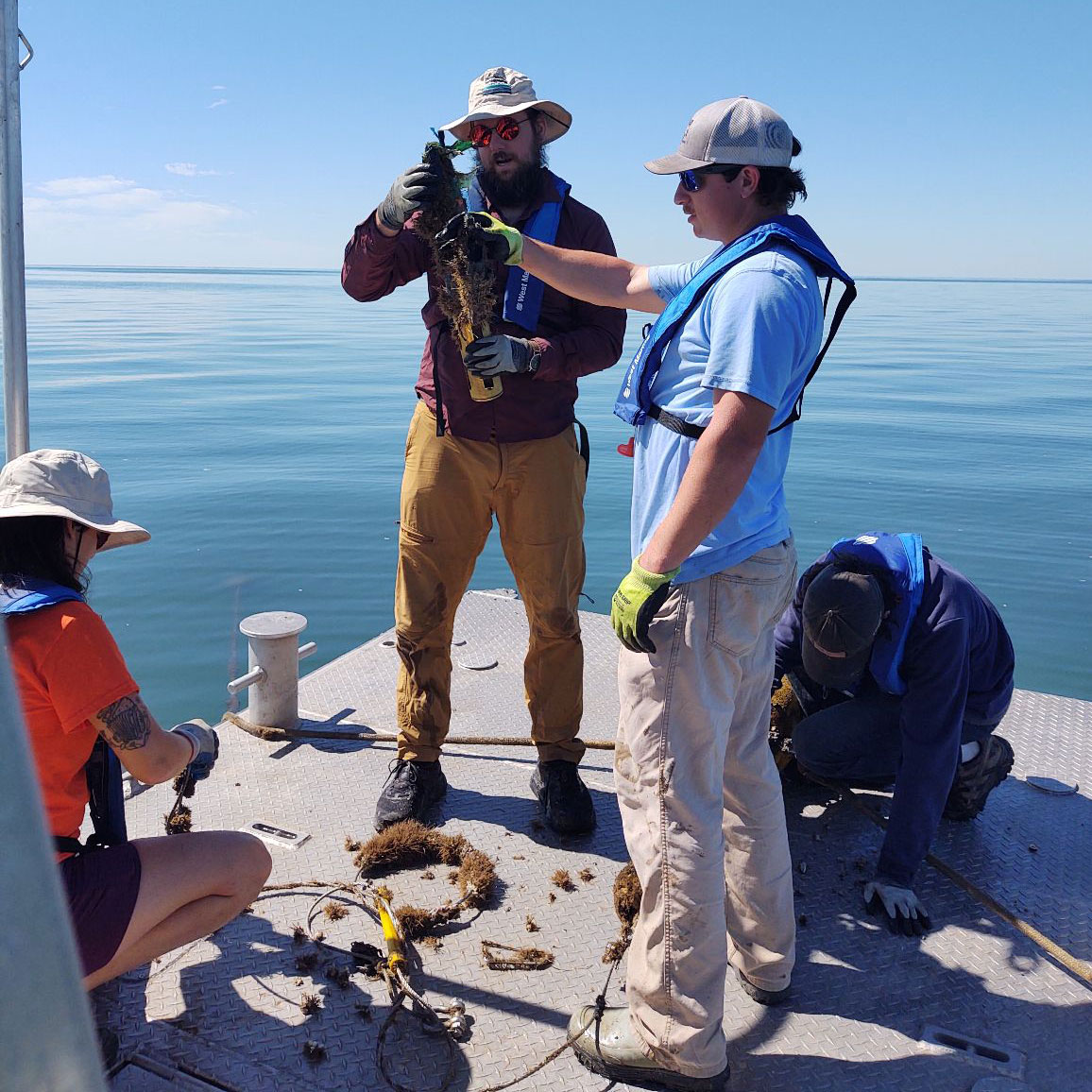

Breton and Chandeleur Sound Hypoxia Study
Since 2010, our coastal team has researched areas of hypoxia in the Breton and Chandeleur Sounds. Hypoxia, or low dissolved oxygen, can occur in natural water bodies due to a number of factors. Hypoxic waters can create “dead zones,” where some marine life cannot survive. Researchers hope to determine the cause of hypoxia in these areas in order to find ways to mitigate it in the future.
Learn More
Hypoxic waters are most prevalent along the coast of the United States from late spring through late summer and are becoming more frequent, widespread, and persistent. In southern Louisiana there has been yearly documentation of a dead zone near the mouth of the Mississippi River. This dead zone has been tied to excess nutrients from the river’s watershed. These nutrients originate in fertilizer and other lawn and farming products, as well as from livestock waste runoff.
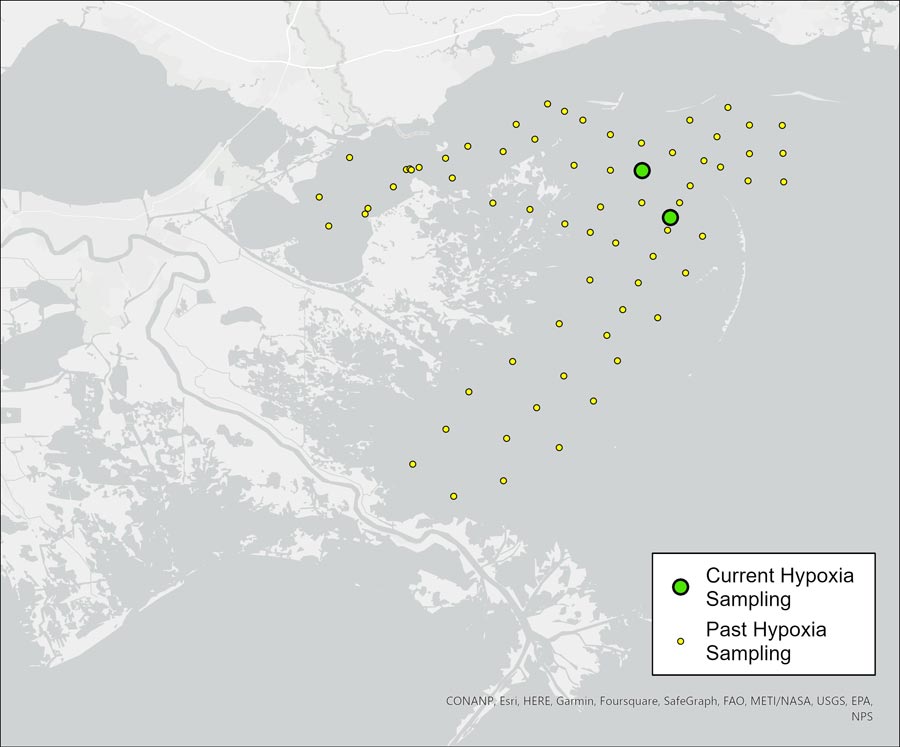
As of 2023, PC scientists are studying the dynamic nature of hypoxia in Chandeleur Sound. Two stations are recording data at 15-min intervals to study how hypoxia sets up in the spring, how extensive it becomes and what factors might be responsible for the hypoxia itself.
As of 2023, PC scientists are studying the dynamic nature of hypoxia in Chandeleur Sound. Two stations are recording data at 15-min intervals to study how hypoxia sets up in the spring, how extensive it becomes and what factors might be responsible for the hypoxia itself.
Major Conclusions
While the size of the hypoxic area in these sounds vary on a yearly basis, it always appears north of the Chandeleur Islands and into the Cat Island Channel. Many factors seem to contribute to this dynamic process, including water quality, winds, tides, currents and rainfall. Each year, the development, expansion and disappearance of the hypoxic area tends to occur in areas cut off from prevailing currents in the Gulf. The cause of the formation of hypoxia may be a naturally induced phenomenon simply due to the lack of wind and wave energy during the summer. It does not appear that the development of bottom hypoxia east of the Mississippi River is driven by the input of excess nutrients, as it is for the Dead Zone. However, the exact cause of this hypoxia has not been found and study continues.